
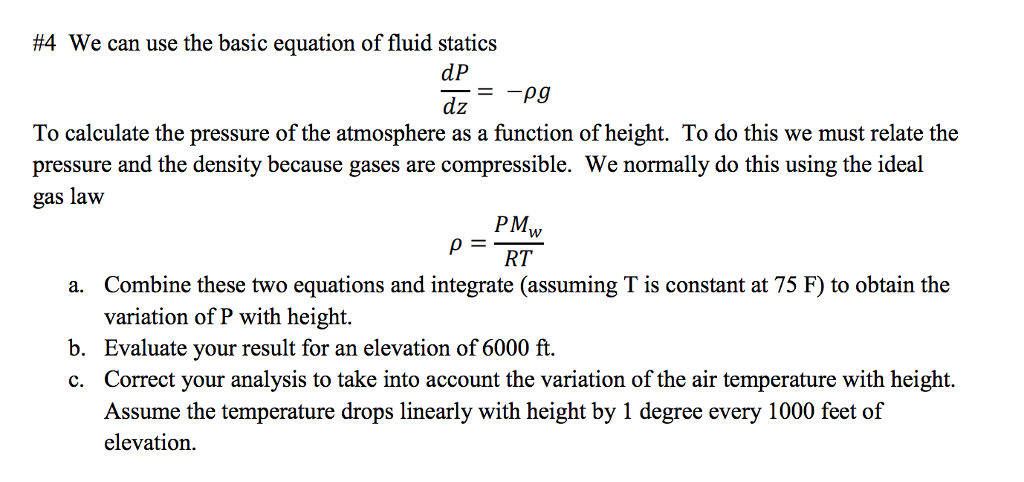
The backup Altimeter System in the face of any disruptive factors that have been affected for safe flight with all systems there is a need for an alternative system. Some destructive factors and geographical factors in the layers of the atmosphere consists of measurements due to deviations in altitude. The aircraft altimeter is basically a barometer measure the height with upon sea level. In order to obtain altitude information in aircraft Pilot-Static system and air data computer is needed. Altimeter reasoned aircraft accidents that occurred before this condition reveals the importance of origin. Safe flight and basic flight instruments altimeter that provides information to pilots to watch for at the level is used as one of. Caputo–Fabrizio was the second best since it yielded an error rate value of 1.97% for a fractional order of derivative α = 1.042, and finally the classical method produced an error rate of 4.36%.Īltitude information is one of the basic elements of safe flight for the aircraft. The experiment has revealed that the Caputo fractional derivative is the most appropriate tool for fitting the model, since it has produced the smallest error rate of 1.74% corresponding to the fractional order of derivative α = 1.005. Then, follow experimental study using real world dataset. Caputo–Fabrizio fractional derivative is the main tool used throughout the proof. First, the proposed model is proven well-defined through existence and uniqueness of its solution. Here, we proposed a new modeling technique of the relationship using Caputo and Caputo–Fabrizio fractional differential equations. There is a consistent literature on this relationship, out of which an ordinary differential equation with initial value problems is often used for modeling. This work is dedicated to the study of the relationship between altitude and barometric atmospheric pressure. Capu-to-Fabrizio was the second best since it yielded an error rate value of 1.97% for a fractional order of derivative α � 1.042, and finally the classical method produced an error rate of 4.36%.įigure 5: Caputo with α � 1.005: the error rate is 1.74%.įigure 6: Caputo with α � 0.99: the error rate is 25.48%. e experiment has revealed that the Caputo fractional derivative is the most appropriate tool for fitting the model, since it has produced the smallest error rate of 1.74% corresponding to the fractional order of derivative α � 1.005. en, follow experimental study using real world dataset. Caputo-Fabrizio fractional derivative is the main tool used throughout the proof. Here, we proposed a new modeling technique of the relationship using Caputo and Caputo-Fabrizio fractional differential equations. ere is a consistent literature on this relationship, out of which an ordinary differential equation with initial value problems is often used for modeling. Is work is dedicated to the study of the relationship between altitude and barometric atmospheric pressure. For different indicated barometric altitudes an evaluation of the density altitude, as a function of non-standards temperature variations and of dew point value, is realized. The first two atmospheric layers (0/11 Km and 11/20 Km) are considered. A brief review of the flight altitudes is performed, and the calculus relations of the density altitude are developed. Also, the paper presents a method to determinate the density altitude with an electronic flight instrument system. The barometric and the hypsometric formulas for the first four atmospheric layers are developed both in the analytical and numerical forms. Further, the atmosphere stratification is presented and the general differential equation, which gives the dependence of the static pressure by the altitude, is deduced. In a short introduction the basic methods used in aviation for altitude determination are nominated, and the importance of the barometric altitude is pointed. The paper is a review of the pressure method used in the aircrafts' altitude measurement.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
